lv thrombus in echo | left ventricular thrombus after heart attack lv thrombus in echo Left ventricular (LV) thrombus formation is a well‐known complication in the course of . Motorcraft MERCON LV is a premium-quality automatic transmission fluid recommended by Ford Motor Company for use in Ford, Lincoln and Mercury vehicles that require MERCON LV type fluid. This product also provides excellent performance in electronically controlled automatic transmissions. Check Owner Guide and .
0 · what is an apical thrombus
1 · lv thrombus treatment guidelines
2 · lv thrombus prevention guidelines
3 · lv mural thrombus treatment guidelines
4 · left ventricular thrombus heart attack
5 · left ventricular thrombus after infarction
6 · left ventricular thrombus after heart attack
7 · anticoagulation for left ventricular thrombus
Fostex Manuals. Voice Recorder. D2424LV MKII. Quick operation manual. Fostex D2424LV Quick Operation Manual. Fostex 24 track digital recorder quick operation guide d2424lv. Also See for D2424LV: Reference manual (162 pages) , Quick operation manual (24 pages) , Brochure (5 pages) 1. 2. 3. Table Of Contents. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. .
what is an apical thrombus
The risk of LV thrombus formation after MI may be greatest in the first 2 weeks, and several studies have found increased incidence of LV thrombus detection by transthoracic echocardiography (or CMR) when performed 1 to 2 weeks after MI (compared with when .¢= @bp ‹ d©Y©_!@»ƒ¬ø˜lêf¶×Gb3æ unyKÒÙr® ƒ ¾îãI¾˜^ .We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
¢= @bp ‹ d©Y©_!@»ƒ¬ø˜lêf¶×Gb3æ unyKÒÙr® ƒ ¾îãI¾˜^ .
Left ventricular (LV) thrombus formation is a well‐known complication in the course of .
eLetters should relate to an article recently published in the journal and are not a .We sought to determine whether an association existed between the .In clinical practice, echocardiography (echo) is widely accepted as the primary screening test .
Clinical, imaging, and pathologic characteristics of left ventricular thrombus: A comparison of .
On the basis of limited data, patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy with LV . Intracardiac thrombi are seen in a variety of clinical settings and can result in .
The risk of LV thrombus formation after MI may be greatest in the first 2 weeks, and several studies have found increased incidence of LV thrombus detection by transthoracic echocardiography (or CMR) when performed 1 to 2 weeks after MI (compared with when performed in the first several days after MI). 16,53–58 Therefore, in patients after MI .Accurate detection of left ventricular (LV) thrombus is important, as thrombus provides a substrate for thromboembolic events and a rationale for anticoagulation. Non-contrast echocardiography (echo) detects LV thrombus based on anatomical appearance.In clinical practice, echocardiography (echo) is widely accepted as the primary screening test for left ventricular thrombus (LVT) . This approach is supported by multiple studies showing that echo performs well as a test for LVT when imaging is tailored for this purpose ( 3–5 ).Clinical, imaging, and pathologic characteristics of left ventricular thrombus: A comparison of contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging, transthoracic echocardiography and transesophageal echocardiography with surgical or pathological validation.
On the basis of limited data, patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy with LV thrombus should be treated with OAC for at least 3–6 months, with discontinuation if LV ejection fraction improves to >35% (assuming resolution of the LV thrombus) or if major bleeding occurs. Intracardiac thrombi are seen in a variety of clinical settings and can result in severe morbidity or even death from embolic events. They can occur following myocardial infarction with ventricular thrombus formation, or with atrial fibrillation .
lv thrombus treatment guidelines
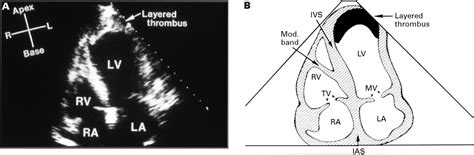
Intracardiac thrombus in the left atrium and atrial appendage (LA/LAA) and left ventricle (LV) increases the risk of systemic thromboembolism and causes potentially devastating diseases such as ischemic stroke and acute ischemia in abdominal organs and lower extremities.Left ventricular (LV) thrombus is a feared complication of LV dysfunction associated with high rates of systemic embolism, morbidity, and mortality. Traditionally, LV thrombus has been associated with acute myocardial infarction (MI).Echo Red Flags: When to suspect LVAD thrombosis Signs of LVAD Dysfunction: •Right‐shift of the IVS and LV enlargement •AoValve opening with every beat (9‐10/10 beats) •Blunted flow through both cannulas (PW/CW Doppler) •RAMP studies (lack of LV dimensions change with increase in pump support/RPM) Left ventricular (LV) thrombus may develop after acute myocardial infarction (MI) and occurs most often with a large, anterior ST-elevation MI (STEMI). However, the use of reperfusion therapies, including percutaneous coronary intervention and fibrinolysis, has significantly reduced the risk.
The risk of LV thrombus formation after MI may be greatest in the first 2 weeks, and several studies have found increased incidence of LV thrombus detection by transthoracic echocardiography (or CMR) when performed 1 to 2 weeks after MI (compared with when performed in the first several days after MI). 16,53–58 Therefore, in patients after MI .
Accurate detection of left ventricular (LV) thrombus is important, as thrombus provides a substrate for thromboembolic events and a rationale for anticoagulation. Non-contrast echocardiography (echo) detects LV thrombus based on anatomical appearance.In clinical practice, echocardiography (echo) is widely accepted as the primary screening test for left ventricular thrombus (LVT) . This approach is supported by multiple studies showing that echo performs well as a test for LVT when imaging is tailored for this purpose ( 3–5 ).Clinical, imaging, and pathologic characteristics of left ventricular thrombus: A comparison of contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging, transthoracic echocardiography and transesophageal echocardiography with surgical or pathological validation. On the basis of limited data, patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy with LV thrombus should be treated with OAC for at least 3–6 months, with discontinuation if LV ejection fraction improves to >35% (assuming resolution of the LV thrombus) or if major bleeding occurs.
Intracardiac thrombi are seen in a variety of clinical settings and can result in severe morbidity or even death from embolic events. They can occur following myocardial infarction with ventricular thrombus formation, or with atrial fibrillation . Intracardiac thrombus in the left atrium and atrial appendage (LA/LAA) and left ventricle (LV) increases the risk of systemic thromboembolism and causes potentially devastating diseases such as ischemic stroke and acute ischemia in abdominal organs and lower extremities.
Left ventricular (LV) thrombus is a feared complication of LV dysfunction associated with high rates of systemic embolism, morbidity, and mortality. Traditionally, LV thrombus has been associated with acute myocardial infarction (MI).Echo Red Flags: When to suspect LVAD thrombosis Signs of LVAD Dysfunction: •Right‐shift of the IVS and LV enlargement •AoValve opening with every beat (9‐10/10 beats) •Blunted flow through both cannulas (PW/CW Doppler) •RAMP studies (lack of LV dimensions change with increase in pump support/RPM)

Hunter (Beedrill) and Chris (Flygon Lv. X) play two of the 2009 World Championship decks. They also talk about the Meta of the era, memories related to certa.
lv thrombus in echo|left ventricular thrombus after heart attack