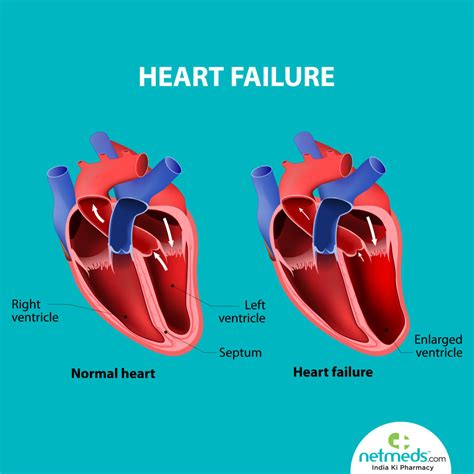
is lv dysfunction heart failure | what does Lv dysfunction mean is lv dysfunction heart failure There are two types of left-sided heart failure: Systolic failure: The left ventricle loses its ability to contract normally. The heart can't pump with enough force to push enough blood into circulation. This is also known as heart failure with reduced ejection, or HFrEF. Hypertrophy means growing (trophy) too much (hyper). Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) makes it harder for the heart to pump blood efficiently. It can result in a lack of oxygen to the heart muscle. It can also cause changes to the heart’s conduction system that make it beat irregularly (arrhythmia).
0 · what is severe Lv impairment
1 · what is moderate Lv impairment
2 · what does Lv dysfunction mean
3 · treatment for severe Lv dysfunction
4 · treatment for left ventricular dysfunction
5 · lvf full form in medical
6 · left ventricular diastolic dysfunction symptoms
7 · impaired Lv function meaning
Gangsta’s Paradise. Coolio. Released November 21, 1995. Gangsta’s Paradise Tracklist. 1. That's How It Is Lyrics. 2. Geto Highlites Lyrics. 3. Gangsta's Paradise (Ft. L.V..
what is severe Lv impairment
The heart's pumping action moves oxygen-rich blood as it travels from the lungs to the left atrium, then on to the left ventricle, which pumps it to the rest of the body. The left ventricle supplies most of the heart's pumping power, so it's larger than the other chambers and essential for normal function. In left-sided or left . See moreRight-sided or right ventricular (RV) heart failure usually occurs as a result of left-sided failure. When the left ventricle fails, increased fluid . See moreCongestive heart failure (CHF) is a type of heart failure which requires seeking timely medical attention, although sometimes the two terms are used interchangeably. See more
Left ventricular dysfunction is the medical name for a weak heart pump. It's a condition that impacts about 9% of people over the age of 60, which is around 7 million .
There are two types of left-sided heart failure: Systolic failure: The left ventricle loses its ability to contract normally. The heart can't pump with enough force to push enough blood into circulation. This is also known as heart failure with reduced ejection, or HFrEF.
Left ventricular dysfunction is the medical name for a weak heart pump. It's a condition that impacts about 9% of people over the age of 60, which is around 7 million Americans. In this Mayo Clinic Minute, Dr. Paul Friedman, a Mayo Clinic cardiologist, explains what the condition is and how it can be diagnosed and treated. Heart failure occurs when the heart muscle doesn't pump blood as well as it should. Blood often backs up and causes fluid to build up in the lungs and in the legs. The fluid buildup can cause shortness of breath and swelling of the legs and feet.Left-sided heart failure occurs when the heart loses its ability to pump blood. This prevents organs from receiving enough oxygen. The condition can lead to complications that include right-sided heart failure and organ damage.
Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is a condition that affects your heart’s ability to fill up with blood before sending the blood out into your circulation. Your heartbeat has.
Left heart failure occurs when there is dysfunction of the left ventricle, resulting insufficient delivery of blood to vital organs.Heart failure can progress, so researchers have identified four stages of the disease — A, B, C and D. Health care professionals also classify heart failure when it has progressed to stages C and D. This classification measures a patient’s overall heart function and severity of symptoms.
Systolic heart failure, also called heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, occurs when your left ventricle can’t pump blood efficiently. It’s a serious condition and can cause damage to other organs. Reduced function of the left ventricle is the most common cause of heart failure. There are two types of left-sided heart failure: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF): This type is also called diastolic heart failure.Left ventricular dysfunction (LVD) with subsequent congestive heart failure (CHF) constitutes the final common pathway for a host of cardiac disorders. Coronary artery narrowing or ischaemic heart disease is the dominant cause of heart failure and is often associated with acute or prior myocardial infarction. There are two types of left-sided heart failure: Systolic failure: The left ventricle loses its ability to contract normally. The heart can't pump with enough force to push enough blood into circulation. This is also known as heart failure with reduced ejection, or HFrEF.
Left ventricular dysfunction is the medical name for a weak heart pump. It's a condition that impacts about 9% of people over the age of 60, which is around 7 million Americans. In this Mayo Clinic Minute, Dr. Paul Friedman, a Mayo Clinic cardiologist, explains what the condition is and how it can be diagnosed and treated. Heart failure occurs when the heart muscle doesn't pump blood as well as it should. Blood often backs up and causes fluid to build up in the lungs and in the legs. The fluid buildup can cause shortness of breath and swelling of the legs and feet.
what is moderate Lv impairment
Left-sided heart failure occurs when the heart loses its ability to pump blood. This prevents organs from receiving enough oxygen. The condition can lead to complications that include right-sided heart failure and organ damage. Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) is a condition that affects your heart’s ability to fill up with blood before sending the blood out into your circulation. Your heartbeat has. Left heart failure occurs when there is dysfunction of the left ventricle, resulting insufficient delivery of blood to vital organs.Heart failure can progress, so researchers have identified four stages of the disease — A, B, C and D. Health care professionals also classify heart failure when it has progressed to stages C and D. This classification measures a patient’s overall heart function and severity of symptoms.
Systolic heart failure, also called heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, occurs when your left ventricle can’t pump blood efficiently. It’s a serious condition and can cause damage to other organs.
Reduced function of the left ventricle is the most common cause of heart failure. There are two types of left-sided heart failure: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF): This type is also called diastolic heart failure.

Hypertrophy means growing (trophy) too much (hyper). Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) makes it harder for the heart to pump blood efficiently. It can result in a lack of oxygen to the heart muscle. It can also cause changes to the heart’s conduction system that make it beat irregularly (arrhythmia).
is lv dysfunction heart failure|what does Lv dysfunction mean